Understanding Joint and Muscle Health: A Comprehensive Guide
01 Sep, 2023
Introduction:
Our joints and muscles are essential components of our bodies, enabling us to move, bend, and perform everyday tasks with ease. However, they are often overlooked until problems arise. Maintaining joint and muscle health is crucial for overall well-being and can greatly impact our quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the fundamentals of joint and muscle health, understand the factors that affect them, and discover practical tips to keep them in top shape.
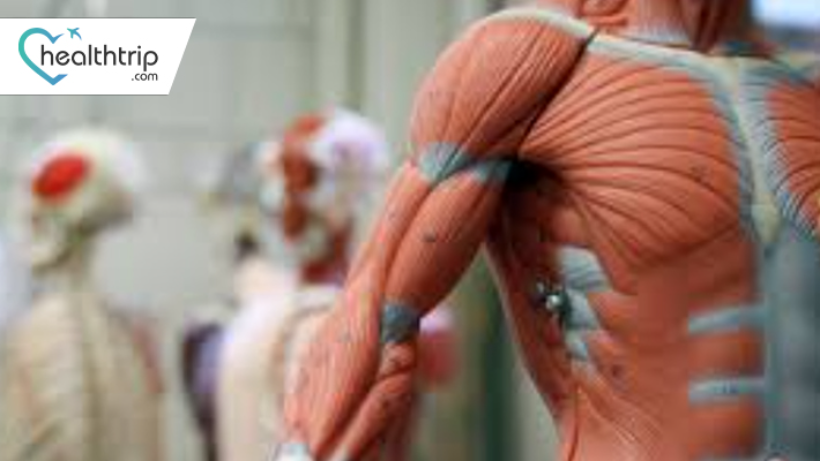
The Anatomy of Joints and Muscles
To understand how to care for your joints and muscles, it's essential to comprehend their structure and function.
Transform Your Beauty, Boost Your Confidence
Find the right cosmetic procedure for your needs.

We specialize in a wide range of cosmetic procedures

Joints: Joints are the connections between bones, allowing for movement. There are several types of joints, including hinge joints (like your knees and elbows), ball-and-socket joints (found in the hips and shoulders), and pivot joints (found in your neck). The cartilage, synovial fluid, ligaments, and tendons play critical roles in joint function.
Muscles: Muscles are responsible for moving your body parts by contracting and relaxing. They come in three types: skeletal (voluntary), smooth (involuntary), and cardiac (found in the heart). Muscles are connected to bones via tendons and play a pivotal role in maintaining posture and performing various tasks.
Factors Affecting Joint and Muscle Health
Understanding the factors that influence joint and muscle health can help us make informed choices to protect them.
1. Age: As we age, joint cartilage can wear down, and muscle mass may decrease. This can lead to stiffness, reduced flexibility, and increased risk of injuries.
2. Diet: Proper nutrition is crucial. Consuming foods rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can help maintain healthy joints and muscles. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and flaxseeds, can reduce inflammation.
3. Exercise: Regular physical activity strengthens muscles and keeps joints flexible. It also promotes the production of synovial fluid, which lubricates joints.
Most popular procedures in
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
Breast Cancer Surger
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory

Total Knee Replaceme
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
Total Knee Replaceme
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
4. Posture: Poor posture can strain muscles and joints, leading to discomfort and long-term damage.
5. Genetics: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to certain joint and muscle conditions, such as arthritis.
6. Injuries: Traumatic injuries or overuse can damage joints and muscles. It's crucial to rest and seek medical attention when necessary.
7. Lifestyle: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can negatively affect joint and muscle health by impairing circulation and promoting inflammation.
Maintaining Joint and Muscle Health
Now that we understand the basics and factors affecting joint and muscle health, let's explore practical steps to keep them in optimal condition.
1. Stay Active: Engage in regular exercise that includes both cardiovascular and strength training. Activities like swimming, yoga, and weightlifting can be particularly beneficial.
2. Maintain a Healthy Diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Consider adding supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin to support joint health.
3. Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration is essential for synovial fluid production, which lubricates joints.
4. Practice Good Posture: Be mindful of your posture when sitting and standing. Ergonomic furniture and workstations can help.
5. Protect Your Joints: Use protective gear when engaging in high-impact activities or sports to reduce the risk of injuries.
6. Listen to Your Body: If you experience pain or discomfort, don't ignore it. Seek medical advice promptly to prevent further damage.
7. Manage Stress: Chronic stress can lead to muscle tension. Incorporate stress management techniques like meditation and deep breathing into your routine.
8. Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol: These habits can contribute to inflammation and hinder the healing process.
9. Get Adequate Rest: Ensure you get enough sleep to allow your muscles and joints to recover.
Common Joint and Muscle Conditions
While proactive care is vital for maintaining joint and muscle health, it's essential to be aware of common conditions that can affect these areas:
1. Arthritis: Arthritis is a group of conditions characterized by joint inflammation. Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout are some of the most common types. Early diagnosis and appropriate management can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further joint damage.
2. Tendinitis: Tendinitis is the inflammation of a tendon, often caused by overuse or repetitive motions. Rest, ice, and physical therapy are typically recommended for treatment.
3. Muscle Strains: Muscle strains occur when muscles are stretched or torn due to overexertion. Proper warm-up and stretching exercises can reduce the risk of strains.
4. Osteoporosis: Osteoporosis weakens bones and makes them more susceptible to fractures. It indirectly affects joint health because fractures can limit joint mobility.
5. Fibromyalgia: Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain and tenderness. It often requires a multidisciplinary approach for management, including medication and lifestyle changes.
6. Bursitis: Bursitis is inflammation of the small, fluid-filled sacs (bursae) that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near joints. Rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications are typically recommended.
7. Back Pain: Back pain can stem from muscle, joint, or spine issues. Proper lifting techniques, core strengthening exercises, and ergonomic adjustments can help prevent and manage back pain.
Seeking Professional Help
If you experience persistent joint or muscle pain, limited mobility, or suspect a more serious issue, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional. They can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend the most suitable treatment options. This may include physical therapy, medications, injections, or in some cases, surgery.
Read for :Comprehensive Orthopedic Care
Remember that self-diagnosis and self-treatment are not advisable when dealing with joint and muscle issues. Seeking professional guidance ensures you receive the right care and prevents the risk of further complications.
How can we help with the treatment?
If you're on the lookout for treatment in India, Thailand, Singapore, Malaysia, UAE, and Turkey, let Healthtrip be your compass. We will serve as your guide throughout your medical treatment. We'll be by your side, in person, even before your medical journey commences. The following will be provided to you:
Global Network: Connect with 35+ countries' top doctors. Partnered with 335+ leading hospitals.
Comprehensive Care: Treatments from Neuro to Wellness. Post-treatment assistance and Teleconsultations
Patient Trust: Trusted by 44,000+ patients for all support.
Tailored packages: Access top treatments like Angiograms.
Real Experiences: Gain insights from genuine patient testimonials.
24/7 Support: Continuous assistance and emergency help.
Our success stories
Conclusion
Your joints and muscles are the foundation of your body's movement and functionality. By understanding their anatomy, taking preventative measures, and seeking timely medical attention when needed, you can maintain their health and continue to enjoy an active and pain-free lifestyle. Ultimately, investing in your joint and muscle health is an investment in your overall well-being. Whether you're an athlete looking to enhance performance, an older adult aiming to maintain mobility, or someone in between, taking care of your joints and muscles should be a lifelong commitment. With the knowledge and strategies provided in this comprehensive guide, you're well-equipped to prioritize and preserve your joint and muscle health for years to come.
Wellness Treatment
Give yourself the time to relax
Lowest Prices Guaranteed!

Lowest Prices Guaranteed!






