A Guide to Gallbladder Cancer: From Symptoms to Treatment
08 Aug, 2023
 Healthtrip Team
Healthtrip TeamGallbladder Cancer
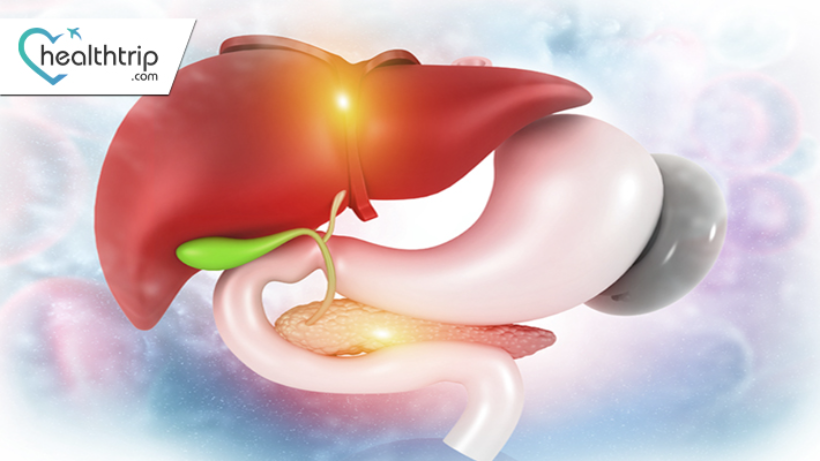
The gallbladder, a small pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver, plays a pivotal role in the digestive system by storing bile. However, like other organs, it's susceptible to malignancies. Gallbladder cancer, although relatively rare, is the most common type of biliary tract cancer. Its early detection is challenging due to the organ's deep-seated location and the often asymptomatic nature of the disease in its initial stages.
Transform Your Beauty, Boost Your Confidence
Find the right cosmetic procedure for your needs.

We specialize in a wide range of cosmetic procedures

Gallbladder cancer cases have been notably observed in various regions worldwide. The prevalence is particularly high among women and those above the age of 60. The reasons for this heightened prevalence are multifaceted, ranging from genetic predispositions to environmental factors.
Different types of Gallbladder Cancer
Understanding the types of gallbladder cancer is crucial for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment approaches. Here's a breakdown:
1. Adenocarcinoma: This is the most common form of gallbladder cancer. It originates from the glandular cells that line the inner surface of the gallbladder. Subtypes include:
- Papillary Adenocarcinoma: Unlike other types, this doesn't spread as quickly and has a better prognosis.
Most popular procedures in India
Atrial septal defect
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory

Coronary Angiogram a
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory

Coronary Angiogram C
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory

Liver Transplant
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
- Mucinous Adenocarcinoma: Characterized by the presence of mucus-producing cancer cells.
2. Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A less common type, it arises from the squamous cells of the gallbladder. It's more aggressive and tends to be diagnosed at a more advanced stage.
3. Adenosquamous Carcinoma: This is a hybrid form, comprising both glandular and squamous cells. Its rarity makes it a subject of ongoing research.
4. Small Cell (Oat Cell) Carcinoma: An extremely rare and aggressive form, it's often diagnosed at an advanced stage, making treatment more challenging.
5. Sarcoma: Originating from the muscle or connective tissue of the gallbladder, sarcomas of the gallbladder are rare but aggressive.
6. Neuroendocrine Tumors: These are rare tumors that arise from the hormone-producing cells in the gallbladder. Their behavior can range from slow-growing to rapidly progressing.
Risk Factors for Gallbladder Cancer
Gallbladder cancer, while relatively rare, has several identifiable risk factors that can increase an individual's likelihood of developing the disease. Recognizing and understanding these factors is pivotal for early detection and prevention.
- Age and Gender -The incidence of gallbladder cancer tends to rise with age, predominantly affecting older adults. Additionally, studies have consistently shown that women are more susceptible to this malignancy than men, possibly due to hormonal factors.
- Gallstones -The presence of gallstones, hardened deposits in the gallbladder, is one of the most significant risk factors. While not everyone with gallstones will develop cancer, a substantial proportion of gallbladder cancer patients have a history of gallstones.
- Chronic Gallbladder Inflammation- Chronic cholecystitis, or long-term inflammation of the gallbladder, can lead to changes in the gallbladder lining, increasing the risk of cancerous transformations.
- Obesity -Elevated body weight has been linked to a higher risk of numerous cancers, including that of the gallbladder. Obesity can lead to an increased production of bile, which might contribute to gallstone formation.
- Family History- Individuals with a family history of gallbladder cancer or gallstones may have an inherited genetic predisposition, elevating their risk.
- Exposure to Certain Chemicals- Occupational exposure to specific industrial chemicals used in the rubber and textile industries has been associated with a heightened risk of gallbladder cancer.
- Gallbladder Polyps- Gallbladder polyps are growths that protrude from the lining of the gallbladder. While most are benign, some, especially those larger than 1 cm, carry a risk of malignant transformation.
Understanding these risk factors is crucial for both medical professionals and the general public. It aids in the early identification of potential cases and the formulation of preventive strategies.
Symptoms of Gallbladder Cancer
Gallbladder cancer often remains undetected in its early stages due to its asymptomatic nature. However, as the disease progresses, several symptoms may manifest:
- Jaundice: One of the most noticeable signs, it results from the buildup of bilirubin in the blood. It causes yellowing of the skin and eyes.
- Abdominal Pain: Patients often experience persistent pain in the upper right or middle part of the abdomen. This pain can sometimes radiate to the back or shoulder blade.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms can be a result of the body's response to the cancer or due to blockage caused by tumor growth.
- Bloating: Some patients report a feeling of fullness or bloating, even after consuming small meals.
- Fever: An unexplained fever might be an indication of an underlying issue, including gallbladder cancer.
- Unintended Weight Loss: A sudden and unexplained loss of weight can be a red flag for several types of cancers, including gallbladder cancer.
- Lumps in the Abdomen: As the disease progresses, one might feel a lump or mass in the abdomen, often resulting from an enlarged gallbladder or liver.
Diagnostic Procedures for Gallbladder Cancer
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Several diagnostic tools and procedures are employed to confirm the presence of gallbladder cancer:
- Ultrasound: This is often the first test done to evaluate the gallbladder. It uses sound waves to produce images of the gallbladder and surrounding structures, helping to identify tumors or stones.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): This imaging test provides detailed cross-sectional images of the body and can help determine the size, shape, and position of any tumors in the gallbladder, as well as their spread to other areas.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Using magnetic fields and radio waves, an MRI provides detailed images of organs and tissues. It's particularly useful for viewing the bile ducts and detecting blockages.
- Biopsy: If imaging tests suggest gallbladder cancer, a biopsy might be performed. During this procedure, a small sample of tissue is removed from the suspected area and examined under a microscope to check for cancer cells.
- Blood Tests: While not definitive for gallbladder cancer, certain blood tests can provide clues. For instance, elevated bilirubin levels might indicate a bile duct blockage.
Conventional Treatment Modalities for Gallbladder Cancer
The treatment approach for gallbladder cancer is multifaceted, depending on the stage of the disease, the patient's overall health, and other factors. Here's a comprehensive overview of the conventional treatment modalities:
1. Surgery
Surgical intervention remains one of the primary treatment options for gallbladder cancer, especially when the disease is detected in its early stages.
- Cholecystectomy: This is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. It's the most common procedure for early-stage gallbladder cancer. The surgery can be performed using a laparoscopic method or through an open surgical approach.
- Radical Gallbladder Resection: For cancers that have spread beyond the gallbladder to nearby tissues or organs, a more extensive surgery might be required. This procedure involves removing the gallbladder, a portion of the liver, and associated lymph nodes.
2. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill or slow the growth of cancer cells. It can be used before surgery to shrink tumors or after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
- Commonly Used Drugs: Some of the drugs used for gallbladder cancer include gemcitabine, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil.
- Side Effects: Chemotherapy drugs can have side effects, including fatigue, nausea, hair loss, and an increased risk of infections due to lowered white blood cell counts.
3. Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. It can be used after surgery to kill any remaining cells or as palliative treatment for advanced cases.
- External Beam Radiation: This is the most common type of radiation therapy for gallbladder cancer. A machine directs high-energy rays at the cancer from outside the body.
- Brachytherapy: This involves placing radioactive material directly into or near the cancer. It's a more localized form of radiation, reducing the risk to surrounding healthy tissues.
4. Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapies are newer treatments that target specific molecules involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells.
- Drugs: Drugs like erlotinib and bevacizumab target specific pathways that cancer cells use to survive and grow. They can be used alone or in combination with chemotherapy.
- Side Effects: These can vary depending on the drug but may include skin problems, high blood pressure, and fatigue.
It's essential for patients to discuss potential risks and benefits of each treatment with their healthcare provider.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies for Gallbladder Cancer
While conventional treatments are primary in managing gallbladder cancer, many patients turn to alternative and complementary therapies to support their overall well-being, alleviate symptoms, and manage side effects.
1. Ayurveda
Originating in India over 3,000 years ago, Ayurveda is one of the world's oldest holistic healing systems. For gallbladder cancer:
- Herbs: Ayurvedic practitioners might recommend herbs like turmeric, which has anti-inflammatory properties, and ashwagandha, known for its potential anti-cancer benefits.
- Treatments: Panchakarma, a detoxifying regimen, might be suggested to cleanse the body and restore balance.
2. Yoga and Meditation
These ancient practices can be beneficial for patients undergoing cancer treatment:
- Yoga: Helps in improving flexibility, reducing muscle tension, and enhancing overall physical health.
- Meditation: Aids in stress reduction, improves mental clarity, and fosters a sense of peace and calm.
3. Homeopathy
This alternative medicine system uses minute doses of natural substances to stimulate the body's healing processes.
- Remedies: Depending on the patient's symptoms and constitution, remedies like Lycopodium, Chelidonium, and Phosphorus might be recommended.
4. Acupuncture
An integral part of traditional Chinese medicine, acupuncture involves inserting thin needles at specific points on the body.
- Benefits: It's often sought for pain management, nausea reduction (especially post-chemotherapy), and balancing the body's energy or 'Qi'.
Nutrition and Diet for Gallbladder Cancer Patients
Proper nutrition plays a pivotal role in supporting the body during and after cancer treatment. It aids in maintaining strength, supporting recovery, and enhancing the quality of life.
1. Importance of a Balanced Diet
A well-balanced diet ensures that the body gets essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals, which can help in tolerating treatment side effects better and speeding up recovery.
2. Foods to Include
- High Fiber: Foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables aid in digestion and provide essential nutrients.
- Lean Proteins: Sources like fish, poultry, tofu, and legumes help in tissue repair and muscle building.
- Antioxidants: Foods rich in antioxidants, like berries, nuts, and green leafy vegetables, help combat oxidative stress.
3. Foods to Avoid
- Processed Foods: These often contain high amounts of salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats.
- Excessive Fats: Limit intake of saturated and trans fats, which can be found in fried foods, certain baked goods, and some margarines.
- Sugars: Excessive sugar can lead to weight gain and energy fluctuations.
It's essential for patients to consult with their healthcare provider before integrating any alternative or complementary therapies into their treatment regimen. This ensures safety and compatibility with ongoing treatments.
Connect with HealthTrip
- Global Network: 35+ countries, 335+ top hospitals, leading doctors of India.
- Diverse Treatments: From Neuro to Cardiac.
- Teleconsultations: $1/minute with leading surgeons.
- Trusted: 44,000+ satisfied patients.
- Packages: Access top packages like Angiograms etc.
- Support: 24/7 assistance, including prompt emergency help.
Our success stories
Rehabilitation and Post-treatment Care for Gallbladder Cancer
Recovery from gallbladder cancer doesn't end once treatment is completed. Rehabilitation and post-treatment care are essential components of the healing journey, ensuring that patients regain their health and quality of life.
1. Physical Therapy
After intensive treatments like surgery or chemotherapy, patients might experience fatigue, muscle weakness, or mobility issues. Physical therapy can:
- Assist in regaining strength and flexibility.
- Provide exercises tailored to individual needs.
- Enhance overall physical well-being and stamina.
2. Counseling
The emotional and psychological aftermath of cancer can be as challenging as the physical aspects. Counseling can:
- Help patients process their experiences.
- Address feelings of anxiety, depression, or fear of recurrence.
- Offer coping strategies and tools for emotional well-being.
3. Support Groups
Connecting with others who've undergone similar experiences can be therapeutic. Support groups:
- Offer a safe space to share feelings and challenges.
- Provide insights into coping strategies and resources.
- Foster a sense of community and understanding.
Key Takeaways
- Early detection and understanding of risk factors are paramount.
- India offers a wide spectrum of treatment options, integrating both modern and traditional methods.
- Medical tourism platforms like HealthTrip make quality treatment both affordable and accessible.
Wellness Treatment
Give yourself the time to relax
Lowest Prices Guaranteed!

Lowest Prices Guaranteed!




