
Bilingual Medical Services: Addressing the Language Gap for Middle Eastern Patients in Thailand
30 Sep, 2023
 Healthtrip Team
Healthtrip TeamIntroduction
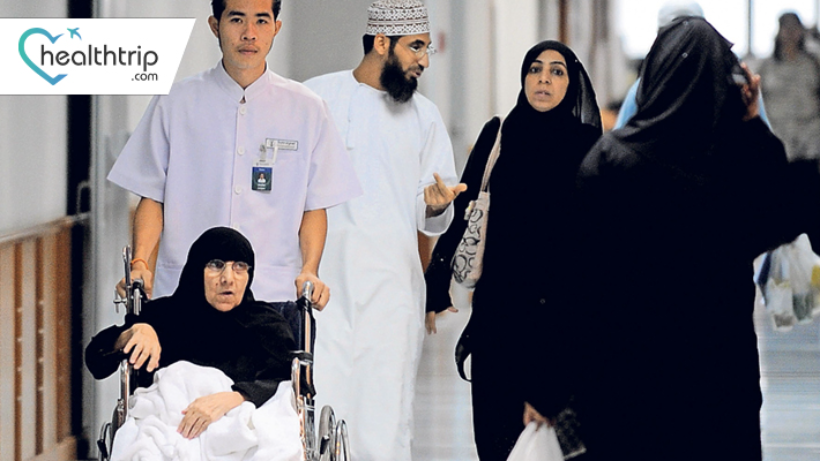
Language is a powerful bridge that connects people across cultures, enabling effective communication and understanding. However, when language barriers exist, especially in crucial domains like healthcare, they can have far-reaching consequences. Thailand, known for its vibrant culture and world-class healthcare system, has witnessed a significant increase in the number of Middle Eastern patients seeking medical treatment. While Thailand's healthcare facilities are renowned for their quality, the language gap between Middle Eastern patients and Thai healthcare providers often poses a challenge. This article explores the importance of bilingual medical services in addressing the language gap for Middle Eastern patients in Thailand.
I. The Language Barrier Challenge
A. Language Barriers and Healthcare Outcomes
Language plays a pivotal role in healthcare. Patients need to convey their symptoms, medical history, and concerns accurately to receive appropriate treatment. For Middle Eastern patients in Thailand, language barriers can hinder this crucial communication, potentially compromising their healthcare experience and outcomes.
Transform Your Beauty, Boost Your Confidence
Find the right cosmetic procedure for your needs.

We specialize in a wide range of cosmetic procedures

B. Language Gap in the Thai Healthcare System
Thailand's healthcare system has made remarkable strides in accommodating international patients. However, the language gap remains a significant concern. Middle Eastern patients, who primarily speak Arabic or Persian, may struggle to communicate effectively with Thai healthcare providers who predominantly use Thai and, to some extent, English. Miscommunication can lead to misdiagnosis, incorrect treatments, and increased patient anxiety.
II. Understanding Cultural Sensitivity
A. Beyond Language: Understanding Cultural Nuances
Beyond language, cultural sensitivity plays a critical role in providing effective healthcare services. Middle Eastern patients often have unique cultural beliefs and expectations regarding healthcare, which can differ from Thai norms. By offering bilingual medical services, healthcare providers can bridge not only the linguistic but also the cultural gap.
B. Importance of Implementing Bilingual Medical Services
Cultural sensitivity involves understanding and respecting the patient's cultural background, beliefs, and practices. Healthcare providers who can communicate with patients in their native language are better equipped to navigate these cultural nuances, providing more holistic care. Moreover, this fosters a sense of trust and comfort for Middle Eastern patients, who may already feel vulnerable in an unfamiliar healthcare system.
III. Benefits of Bilingual Medical Services
1. Facilitating Enhanced Communication
The primary benefit of bilingual medical services is improved communication between patients and healthcare providers. When patients can express themselves in their native language, healthcare providers can gain a clearer understanding of their medical history, symptoms, and concerns, leading to more accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
2. Elevating Patient Comfort Levels
Language barriers can create stress and anxiety for patients. Bilingual medical services alleviate this burden by making patients feel more at ease during their medical consultations. This increased comfort level can positively impact patient outcomes.
3. Enhanced Cultural Competency:
Bilingual healthcare providers who understand Middle Eastern cultures can provide care that is culturally sensitive and tailored to the patient's needs. This fosters a sense of trust and respect between the patient and the healthcare team.
Most popular procedures in India
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
ANGIOGRAM
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory

ASD Closure
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory

4. Enhancing Overall Patient Satisfaction
Patients who receive care in their native language and feel understood are more likely to be satisfied with their healthcare experience. High patient satisfaction not only benefits the individual but also enhances the reputation of the healthcare facility.
5. Boosting Attractiveness for Medical Tourism
Thailand has become a hub for medical tourism, attracting patients from around the world. By offering bilingual medical services, Thailand can cater to a broader international audience, increasing its competitiveness in the global healthcare market.
IV. Implementation of Bilingual Medical Services
To address the language gap for Middle Eastern patients in Thailand effectively, several steps can be taken:
1. Strategic Recruitment and Training
Healthcare facilities should prioritize the recruitment of bilingual staff, including doctors, nurses, and interpreters who are proficient in Arabic, Persian, or other Middle Eastern languages. These professionals should also receive cultural competency training to provide holistic care.
2. Translation and Interpretation Services:
Implement translation services for medical documents, forms, and informational materials. Ensure that these translations are accurate and culturally sensitive. Offer on-site or remote interpretation services for medical consultations. This allows healthcare providers to communicate effectively with patients who do not speak Thai or English.
3. Multilingual Patient Support Strategies
Designate multilingual patient support staff who can assist Middle Eastern patients with administrative tasks, appointment scheduling, and navigating the healthcare system.
4. Cultural Awareness Programs:
Conduct regular cultural awareness programs for healthcare staff to educate them about Middle Eastern customs, traditions, and healthcare expectations.
5. Establishing a Robust Feedback Mechanism
Establish a feedback mechanism where patients can express their concerns about language and cultural barriers. Use this feedback to continuously improve bilingual medical services.
V. Challenges in Implementing Bilingual Medical Services:
1. Allocating Resources Effectively
Implementing bilingual medical services requires a significant investment in recruiting and training bilingual staff, providing translation and interpretation services, and cultural competency training. Healthcare facilities may face budget constraints that hinder their ability to allocate resources effectively.
2. Availability of Bilingual Healthcare Professionals:
Finding healthcare professionals who are proficient in Middle Eastern languages and culturally sensitive can be challenging. Recruiting and retaining such staff members can be a long-term challenge for healthcare facilities.
3. Ensuring Quality in Translation and Interpretation
Ensuring the accuracy of translation and interpretation services is crucial. Miscommunication due to errors in translation or interpretation can lead to serious medical mistakes. Maintaining a high standard of quality in language services is a continuous challenge.
4. Continual Improvement in Cultural Competency
Cultural competency training is essential, but it may not guarantee a deep understanding of the diverse cultural backgrounds of Middle Eastern patients. Healthcare providers must continually educate themselves and adapt to the unique needs and expectations of these patients.
5. Balancing Technology Integration
Leveraging technology for interpretation services can be challenging, particularly in emergency situations where immediate in-person interpretation is necessary. Healthcare facilities need to strike a balance between technology and human resources.
6. Safeguarding Patient Privacy
Ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of patient information when using interpreters or translation services can be complex. Healthcare providers must take extra precautions to maintain the security of patient data.
VI. Success Stories in Implementing Bilingual Medical Services:
1. Improving Patient Outcomes Through Effective Communication
Healthcare facilities that have successfully implemented bilingual medical services report better patient outcomes. Patients can communicate their symptoms and concerns more effectively, leading to more accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
2. Sustaining High Levels of Patient Satisfaction
Hospitals that prioritize language and cultural sensitivity consistently receive high marks in patient satisfaction surveys. Patients appreciate being heard and understood, which contributes to their overall satisfaction with the healthcare experience.
3. Driving Increased Medical Tourism to Thailand
Thailand's efforts to provide bilingual medical services have led to an increase in medical tourism from Middle Eastern countries. Word-of-mouth recommendations and positive experiences draw more patients to Thailand's healthcare facilities.
4. Cultivating a Positive International Reputation
Healthcare facilities that excel in providing bilingual services gain a positive reputation not only among Middle Eastern patients but also within the international healthcare community. This enhances the country's standing as a global healthcare destination.
5. Fostering Long-Term Partnerships with Middle Eastern Countries
Success in addressing the language gap can lead to long-term partnerships and collaborations with Middle Eastern countries, including government agencies, healthcare providers, and educational institutions. This can further enhance the exchange of medical knowledge and expertise.
6. Cultural Competency and Sensitivity:
Healthcare providers who undergo cultural competency training and work with diverse patient populations become more culturally sensitive and adaptable. This skill set extends beyond Middle Eastern patients and benefits all patients in their care.
Conclusion
The growing influx of Middle Eastern patients in Thailand's healthcare system presents both opportunities and challenges. While Thailand offers world-class medical facilities, addressing the language gap is crucial to ensure that Middle Eastern patients receive the quality care they seek and deserve.
Bilingual medical services not only bridge the language divide but also promote cultural sensitivity and enhance the overall healthcare experience for Middle Eastern patients. By implementing strategies such as recruiting bilingual staff, offering translation and interpretation services, and fostering cultural awareness, Thailand can position itself as a leader in providing inclusive and patient-centred healthcare to a diverse international clientele.
Wellness Treatment
Give yourself the time to relax
Lowest Prices Guaranteed!

Lowest Prices Guaranteed!
